 These activities are intended to prevent fish and other aquatic organisms becoming trapped in intakes for hydropower turbines, water abstraction points and pumping stations, as they move through a watercourse.
These activities are intended to prevent fish and other aquatic organisms becoming trapped in intakes for hydropower turbines, water abstraction points and pumping stations, as they move through a watercourse.
Techniques
There are a wide range of techniques that can be used to implement this environmental improvement, depending upon the type and characteristics of the water body in which it is going to be applied:
- Installing physical fish and eel screen on turbines, intakes and pumps
- Installing systems to discourage fish from entering abstraction equipment, including acoustic barriers, lighting barriers and bubble curtains
- Installing fish and eel passes (including bypass channels), so the pumps can be safely avoided
Benefits
Managing the risk of fish entrainment can deliver a range of direct and indirect benefits, including:
- Direct benefits for fish and eel populations
- Maintenance of biodiversity within the watercourse
- Potential benefits for commercial and recreational fisheries within the watercourse
- Reduction of the likelihood for emergency maintenance of hydropower, abstraction and pumping equipment
- Reduced costs of maintenance of abstractions points and pumps
Case Study Benefits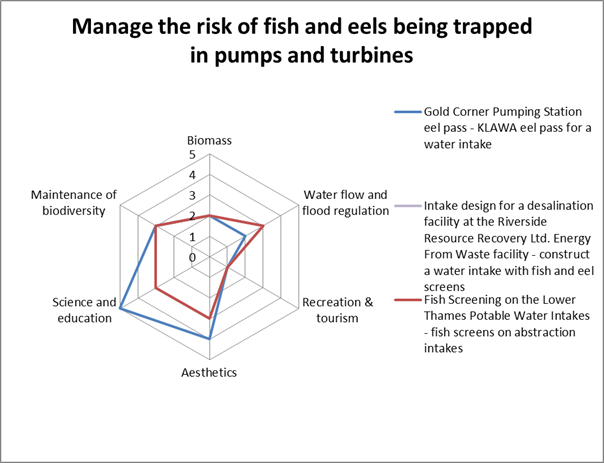
This diagram displays a comparison of benefits scores (using a high-level ecosystem service assessment methodology) associated with the techniques used in each case study. More details on the methodology can be found here.
(Please note: the Riverside Resource Recovery case study scored the same as the Thames Portable Water Intakes case study so is not visible due to overlap of lines)