This activity covers both the construction of new soft bank face protection for flood and erosion defence purposes, and the replacement of hard bank protection with a softer solution, involving bank rehabilitation / reprofiling.

This needs to be considered in parallel with either channel realignment or channel shape changes to reduce erosion in vulnerable areas.
On transitional and coastal waters, this activity can include the alteration / removal of rip-rap as an alteration to the water’s edge.
River Cole image @ Environment Agency copyright and database rights 2013
Techniques
There are a wide range of techniques that can be used to implement this environmental improvement, depending upon the type and characteristics of the water body in which it is going to be applied. These include:
- Removal of hard bank protection and reprofiling of banks to avoid the need for additional protection
- Removal of hard bank protection and replacement with a soft engineering technique that is suitable for the watercourse
- Planting of suitable native species to enhance existing habitats and create new ones
- Creation of aquatic ledges instead of hard bank protection
- Create backwaters and online wetlands to increase habitat diversity
- Create buffer strips to improve or preserve riparian and bankside habitats, and increase bank stability
Benefits
Improvements to water’s edge and bank side habitats can deliver a wide range of direct and indirect benefits, including:
- Direct benefits to plants, invertebrates, birds and animals which live on the banks and riparian zone
- Improvements to in-channel habitats for aquatic plants, fish and invertebrates
- Improvements to the physical habitat conditions of the watercourse, including the creation of a more natural bank profile and the creation of more varied habitat niches
- Restoration of natural processes, including erosion and deposition
- Improvements to the aesthetic value of the watercourse and improvements to its recreational value
- Reduction in maintenance costs of hard defences
Case Study Benefits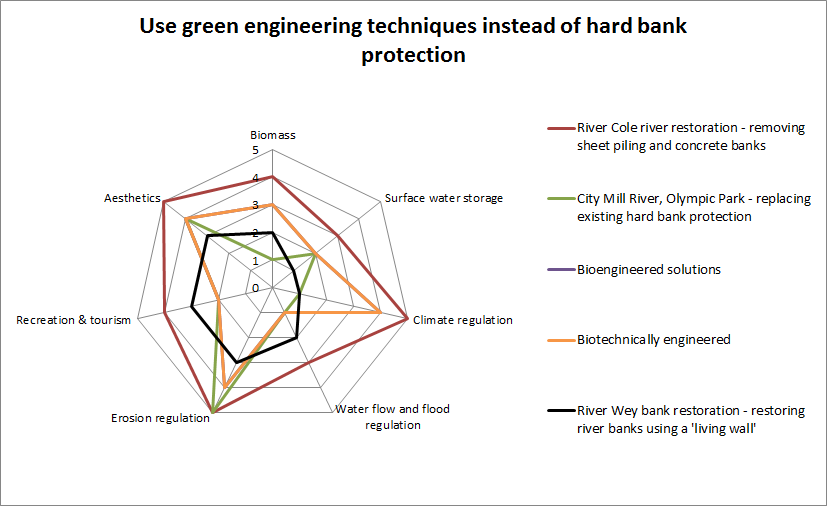
This diagram displays a comparison of benefits scores (using a high-level ecosystem service assessment methodology) associated with the techniques used in each case study. More details on the methodology can be found here.